Network connections: Everything you need to know

Network connections are the backbone of our digital world, allowing devices like computers and phones to communicate and share data.
This guide explains what a network connection is, the different types of connections, how to fix common problems, and how to keep your connection secure.
What is a network connection?
A network connection is the established link between two or more devices, often using standard protocols like Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP) to communicate or share data. It can be established through cables or wirelessly and provides the foundation for all network communication, from a simple local area network (LAN) setup to the global internet as we know it.
The purpose of a network connection is to allow devices to communicate and share data or resources. These resources can include an internet connection, files on a server, or peripherals like a printer. A connection creates a communications path that allows data to travel between connected devices.
Network connections operate on different scales. A local network connection in a LAN connects devices within a limited area like a home or office. In contrast, a wide area network (WAN) allows network connections between devices over a large geographical area. For example, a company with offices in multiple countries can set up a WAN to connect all of its LANs.
How network connections work
Network connections work by breaking down data into smaller pieces called packets, which contain a portion of the original data called the payload and a header with crucial information like the source and destination of the packet.
Hardware plays a critical role in directing these packets within a network connection. Every network-capable device has a unique physical address called a Media Access Control (MAC) address for local identification. This helps a network identify where data packets need to be sent or received from.
The whole process is governed by a set of rules called protocols, the most common of which is the internet protocol suite, or TCP/IP. TCP manages the breakdown and reassembly of data into packets, as well as maintaining a connection between a source and its destination. IP handles the addressing, routing, and delivery of these data packets.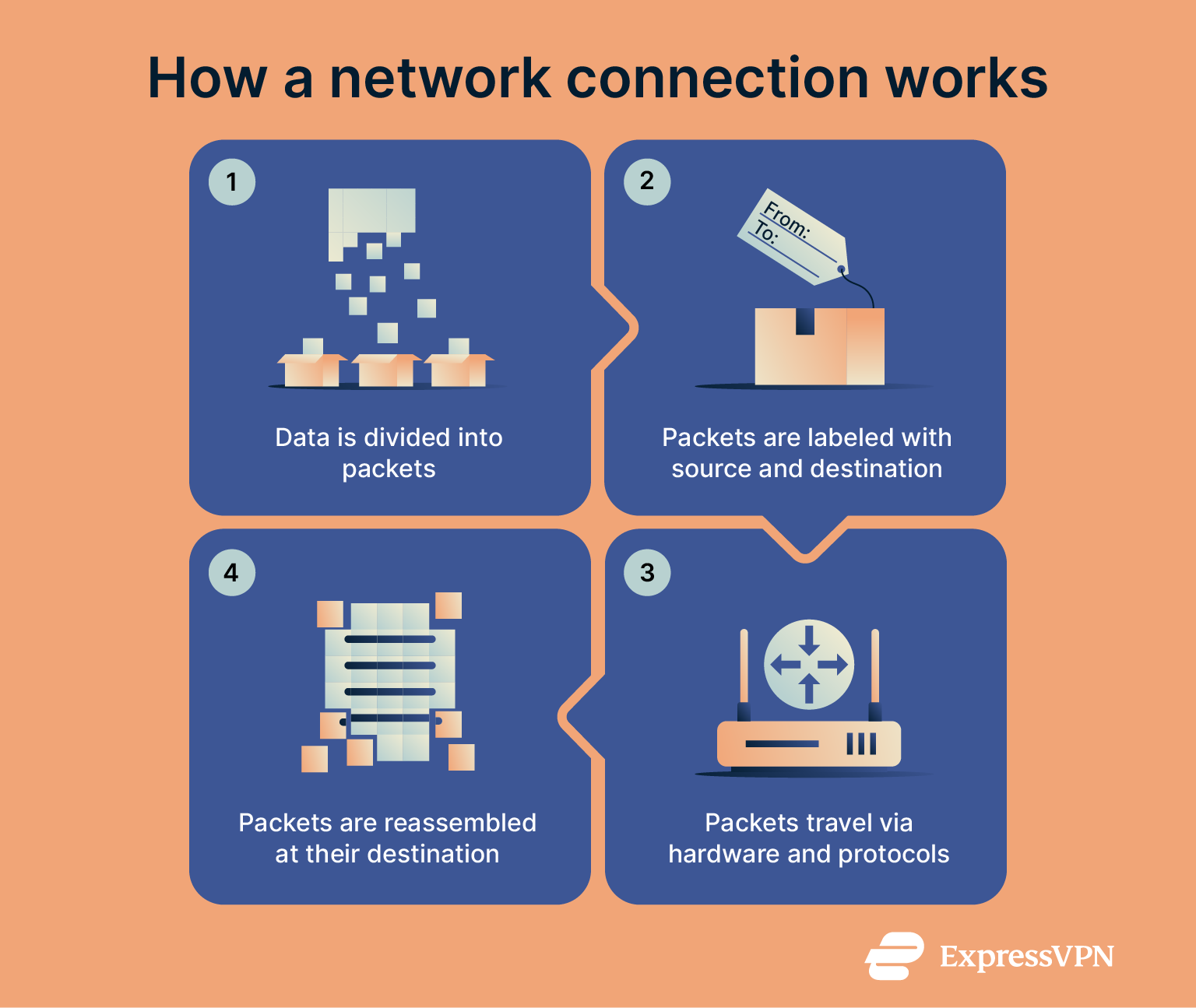
Types of network connections
Network connections are broadly categorized into two main groups: wired and wireless. Each type uses different technologies to transmit data and offers distinct advantages depending on the speed, mobility, and reliability needs.
Wired connections
Wired connections rely on physical cables to transfer data between devices. This physical link generally provides a stable and fast connection, making wired connections a preferred choice for activities that demand fast and consistent performance, like online gaming.
Ethernet
Ethernet is the most widely used technology for wired local LANs. It uses twisted-pair copper cables and RJ45 connectors to link devices to a router or network switch.
Most modern Ethernet connections support gigabit speeds, or 1,000 megabits per second (Mbps). Newer standards are pushing speeds even higher to 10Gbps (CAT6) and even 40Gbps (CAT8).
Fiber optics
Fiber optic cables are made of strands of glass that are about as thin as human hair. They allow data to be sent as pulses of light and enable extremely fast data transmission over long distances without drops in speed. Fiber optic cables form the backbone of modern-day networking infrastructure and are capable of transmission rates of up to 800Gbps.
Wireless networks
Wireless networks provide network connectivity without physical cables, using radio waves to transmit data through the air. This enables more mobility and convenience, but it comes at the cost of potentially slower speeds or higher latency than wired connections.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that connects devices to a LAN using radio waves. Routers broadcast these signals on specific frequency bands like 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
Wi-Fi technology is constantly evolving through new standards defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Standards like Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) can broadcast on the 6GHz frequency band and offer significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and support for more devices.
Cellular networks (4G/5G)
Cellular networks enable mobile devices to connect to the internet over vast distances using a system of cell towers that transmit and receive signals between the network and its connected devices.
Cellular networks have evolved through multiple generations, each bringing major technical improvements. 4G (LTE) surfaced in the late 2000s, with speeds that made high-quality video streaming, mobile gaming, and app-driven services practical on smartphones.
5G became commercially available in 2019. It’s capable of gigabit speeds and much lower latency compared to 4G.
Common network and connectivity issues
Connection problems are common whether you’re using a wired or wireless network connection.
What are the symptoms of a network connection problem?
Network connection problems manifest in several ways, from a complete outage to a subtle decline in performance. The following are the most common signs that something is wrong with your network connection:
- No internet access: Your device may show that it’s connected to a network, but web pages will not load. This simply means that you have no internet access, even though your device is connected to your local network.
- Slow speeds: If websites take a long time to load, videos constantly buffer, or downloads move at a crawl, you are likely experiencing a slow internet connection.
- Frequent disconnections: Your connection may drop randomly, forcing you to reconnect your device. These intermittent drops can be caused by Wi-Fi signal interference or router problems.
- Application-specific failures: The issue can sometimes be isolated to a single service. One app might not connect even though the internet and other apps are working fine.
How to fix internet connection issues
Below are the various approaches you can take to resolve network connection issues in wired or wireless connections.
Fixing home network connection
For a home Wi-Fi or wired connection, the following steps should help you resolve common problems:
- Restart equipment: The most effective first step is to power cycle your modem and router. Unplug both devices from their power source, wait for at least 60 seconds, and then plug them back in before trying to connect again.
- Check cables: Ensure that all Ethernet and power cables are securely plugged into your router, modem, and computer. A loose or damaged cable can often cause connection problems.
- Improve your Wi-Fi signal: If you are on Wi-Fi, move closer to your router. You could also consider repositioning your router to a more central location in your home. Another alternative is getting a mesh network to improve coverage across your house.
- Use built-in troubleshooters: Both Windows and macOS have network diagnostic tools that can automatically detect and fix problems. You can typically find these tools in the network settings section of your operating system.
Fixing mobile network issues
If you have network connection issues on your smartphone’s mobile network, these troubleshooting steps can help restore your service:
- Toggle airplane mode: Turn on airplane mode for about 30 seconds and then turn it off. This action forces your phone to disconnect and look for the best cellular connection in the area.
- Restart your phone: A simple reboot can resolve temporary software glitches that may be interfering with your phone's ability to connect to the network.
- Reset network settings: If problems persist, you can reset your phone’s network settings. This will erase all saved cellular configurations and might fix stubborn connectivity issues.
- Re-insert your SIM card: Power off your device, remove the SIM card, and then place it back in its tray. An improperly seated SIM card can prevent your phone from registering on the network.
Network connection security tips
A secure network connection is essential for protecting your privacy and sensitive data. In 2024, in the U.S. alone, cybercrime affected hundreds of thousands of people and led to losses of over $16 billion, highlighting the need for strong security practices.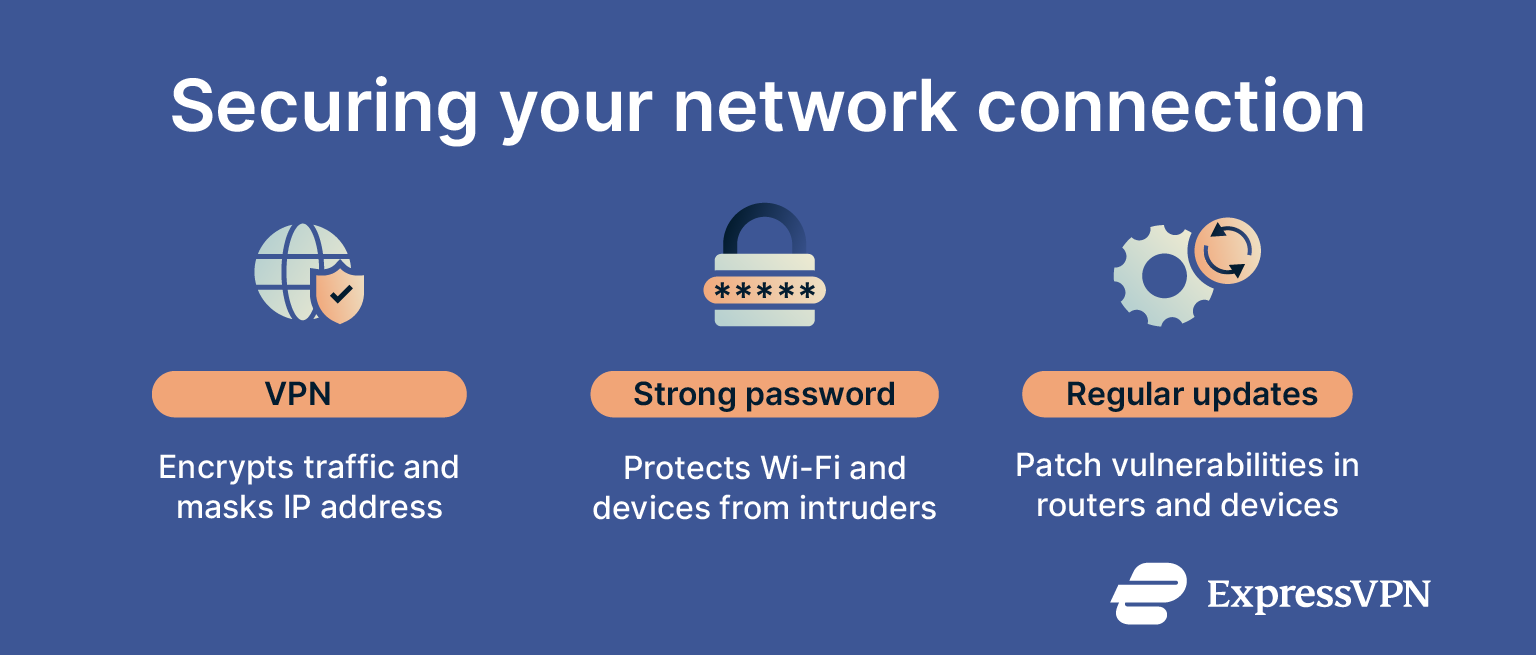
VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) is one of the most effective tools for securing your network connection. It works by creating an encrypted tunnel for all your online traffic. This encryption prevents your internet service provider (ISP), advertisers, and other third parties from monitoring your activity.
If you're wondering if you need a VPN, the added layer of security is a compelling reason to get one.
Strong password
Your Wi-Fi password, also known as a network security key, is the first line of defense for your home network. A weak, easily guessable password allows unauthorized individuals to access your network, use your internet, and potentially spy on your activity.
You should change the default administrator password on your router to prevent unauthorized changes to your network settings. The new password should be long and complex.
In fact, this rule applies to all your online accounts and not just the Wi-Fi. The easiest way to keep track of several strong passwords is to use a reliable password manager like ExpressKeys. Alongside helping you create and securely store passwords, it autofills them on websites for convenience.
Regular updates
The software that runs your router, also known as firmware, needs to be up to date at all times. Router manufacturers release firmware updates to patch security holes, fix bugs, and improve performance.
FAQ: Common questions about network connections
What is a network connection?
A network connection is an established link between two or more devices that lets them communicate and share resources. It’s the fundamental technology that enables everything from a local area network (LAN) to the global internet.
How can I fix my network connection?
There are various steps you can follow to fix your network connection, like restarting your equipment, checking your cables, moving to a place with better Wi-Fi coverage, toggling airplane mode, or re-inserting your SIM card if you’re using mobile data.
What are the common types of network connections?
The most common types of network connections fall into two categories. There are wired network connections, which include Ethernet and fiber optics to establish physical connections, and wireless connections, which include Wi-Fi and cellular networks like 4G or 5G.
How do wired and wireless networks differ?
Wired networks use cables to provide faster speeds, lower latency, and greater reliability. Wireless networks offer the convenience of connecting devices without cables, providing mobility and flexibility. The choice between them is a trade-off between maximum performance and convenience.
What factors impact network connection performance?
Several factors impact performance, including the speed of your internet plan, the number of devices using the network, and your router's capabilities. For wireless connections, performance is also affected by your distance from the router and physical obstructions like walls, which can weaken the signal.
What are the best practices for securing your network?
To secure your network, use a VPN to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data from snoops. You should also use a strong, unique password for your Wi-Fi network and regularly update your router's firmware to protect against the latest security threats.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN